
|
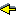
| typexpr | ::= | ' ident |
| | | _ | |
| | | ( typexpr ) | |
| | | [[?]ident:] typexpr -> typexpr | |
| | | typexpr { * typexpr }+ | |
| | | typeconstr | |
| | | typexpr typeconstr | |
| | | ( typexpr { , typexpr } ) typeconstr | |
| | | typexpr as ' ident | |
| | | [ variant-type ] | |
| | | < [..] > | |
| | | < method-type { ; method-type } [; ..] > | |
| | | # class-path | |
| | | typexpr # class-path | |
| | | ( typexpr { , typexpr } ) # class-path | |
| poly-typexpr | ::= | typexpr |
| | | { ' ident }+ . typexpr | |
| method-type | ::= | method-name : poly-typexpr |
| Operator | Associativity |
| Type constructor application | -- |
| * | -- |
| -> | right |
| as | -- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| variant-type | ::= | [ | ] tag-spec { | tag-spec } |
| | | > [ tag-spec ] { | tag-spec } | |
| | | < [ | ] tag-spec-full { | tag-spec-full } [ > { `tag-name }+ ] | |
| tag-spec | ::= | `tag-name [ of typexpr ] |
| | | typexpr | |
| tag-spec-full | ::= | `tag-name [ of typexpr ] { & typexpr } |
| | | typexpr |
|
|
|


