CS307: Texture Mapping 1: Simple Image Mappings
Plan
- Overview of texture mapping
- Mapping an image onto a plane
- CORS and setting up a local server
- Exercise: Loading image files on your local machine
- Exercise: Mapping multiple floral images
- Exercise: A room with a view
- Next time: Repeating textures, the Texture Tutor, and synthetic textures
Texture Mapping Recap
- At its most basic, a texture is an array of pixels. So is an image. A texture can be a synthetically generated pattern of lightness or color, or an image taken from a camera.
- A texture pattern can be mapped or "painted" onto any surface.
A texture pattern is typically a 2D thing, but can be mapped onto
2D or 3D surfaces.
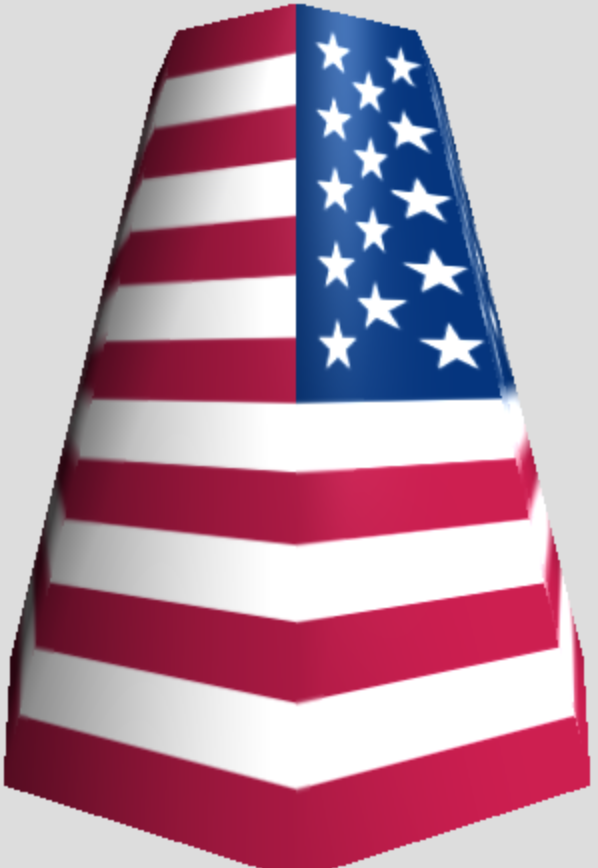
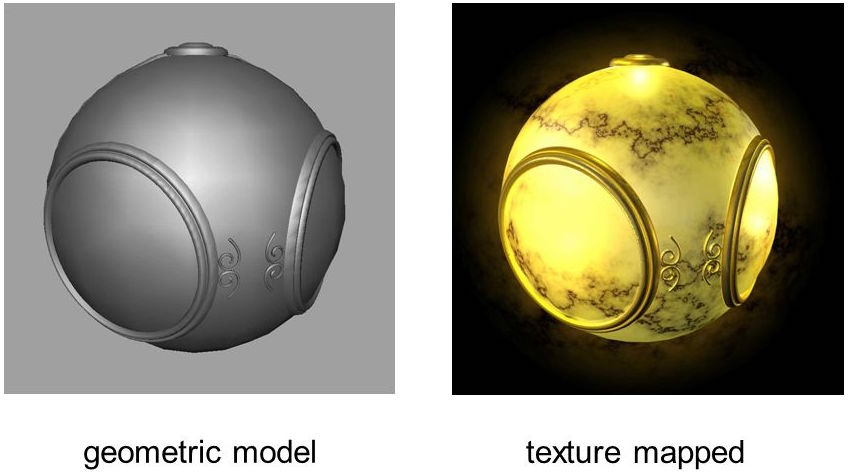

- Each vertex of a triangular face can have texture parameters. Typically, the texture parameters for a whole geometry go from 0-1 (but not always), and the texture parameters for faces are interpolated.
- When loading textures from an image, we need to consider that it takes a non-negligible amount of time for the image to load, so we will need to write event handlers for the after load event.
Mapping an Image onto a Plane
Consider this relaxing floral scene in which a single image is mapped onto three planes.
Three.js has a THREE.TextureLoader class to load an image
to be used for texture mapping, which enables us to provide an event handler
that among other things, can render the scene after the image load is complete.
This is the key code in the floral display example:
var loader = new THREE.TextureLoader();
loader.load("relaxation.jpg",
function (texture) {
displayPanels(texture);
} );
The image is stored in a THREE.Texture object that is passed as
input to an anonymous function (the event handler) that is provided as the second
input to the load() method.
Here is the definition of the displayPanels() function, which
renders the scene at the end:
function displayPanels (texture) {
// plane geometry with texture-mapped floral image
var planeGeom = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(10,10);
var planeMat = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial(
{color: 0xffffff,
map: texture} );
var planeMesh = new THREE.Mesh(planeGeom, planeMat);
scene.add(planeMesh);
// repeat texture mapping on right panel
var planeMeshR = planeMesh.clone();
var dist = 5*Math.cos(Math.PI/4);
planeMeshR.position.set(5+dist, 0, dist);
planeMeshR.rotation.y = -Math.PI/4;
scene.add(planeMeshR);
// repeat texture mapping on left panel
var planeMeshL = planeMesh.clone();
planeMeshL.position.set(-5-dist, 0, dist);
planeMeshL.rotation.y = Math.PI/4;
scene.add(planeMeshL);
TW.render(); // render the scene
}
Three.js requires that images used for texture mapping have dimensions that are powers of 2. In this example, the image has 256x256 pixels, and it is mapped onto square planes.
CORS and Setting up a Local Server
Before we launch into our first exercise, we need to deal with a bit of unpleasantness called CORS, for Cross-Origin Resource Sharing. The problem arises because, for security reasons, JavaScript is not allowed to do what the browser can do: request resources from another domain.
What this means for us is:
Your images and your html file have to be in the same domain.
This means you can't work with textures on your local machine without setting up a server. Fortunately, this is easy.
There's more about CORS in the
next reading, but we'll do an
exercise here to demonstrate the problem and solution. We'll use
the Run Local Server
option, using Python, described in the Three.js
documentation.
Exercise: Loading image files on your local machine
Save the flower-display.html code file on your Desktop (be sure to save it as Webpage, HTML Only). Also save this image into your Desktop (be sure to keep the same filename).
Open your local flower-display.html file in your browser and observe the
error message that appears in the JavaScript Console.
Now follow these steps to run a local server on your Mac or laptop:
- Start a terminal window
-
cdto the directory that has your downloaded HTML file in it, in this casecd ~/Desktop. - Start a web server on port 8000 (by default) using Python:
python -m SimpleHTTPServer - Go back to your web browser and try the following URL:
http://localhost:8000/flower-display.htmlYou should now see the display of three panels with the flower scene.
Mapping Multiple Images onto Scene Objects
The TW package provides a helper function, TW.loadTextures()
that takes an array of URLs for multiple image files and a callback function as
inputs, and invokes the function on an array of THREE.Texture objects
that store the multiple images.
Here is some skeleton code:
TW.loadTextures(["image1.jpg", "image2.jpg", ...],
function (textures) {
...
} );
You do not need to create a THREE.TextureLoader object in this
case, as TW does this for you.
Exercise: Mapping multiple floral images
- Save these flower1.jpg and flower2.jpg images on your Desktop.
- Create a copy of your
flower-display.htmlcode file under a new name, and modify the new file to load all three images of floral scenes and place them on the three different planes in the scene.Remember that the texture is part of the material, so you'll need create three different materials, instead of just cloning the mesh.
- Your solution might like like this flower-display3.html
Exercise: A Room with a View
This exercise illustrates how you can use a THREE.BoxGeometry to
create a room.
- To begin, save this room-start.html code file to
your Desktop, along with this
seaScape.jpg image.
The code creates a
THREE.BoxGeometryobject with sides that have 6 different colors. - Change the basic materials for the cube faces to
THREE.MeshLambertMaterial, and set thesideproperty for the material toTHREE.BackSide(this is all that's needed to convert the box to a room that can be viewed from the inside!) - Add code to create a white point light source, position this light in the center of the room, and add it to the scene
- Complete the definition of the
displayView()function, which should map an image (stored in the inputTHREE.Textureobject) onto a plane that is the same size as each side of the room, position the plane at the back wall of the room, and render the scene - Feel free to select a nicer set of colors for the walls of the room!
Your solution might look like this room-with-view.html scene
(Optional)
In the above solution, we cheated a bit, creating something like
a sheet of wallpaper that was placed at the location of the back
wall. We can also
directly map an image texture onto one or more sides (faces) of the box.
Modify the definition of the displayView() function so
that it maps the input texture directly onto the back wall of the box,
before rendering the scene. You can just comment out your existing
code and replace it with a single code statement.
Some hints:
THREE.Mesh objects have a material
property. In the case of meshes with multiple materials, the value of
this property is an object that itself has a property
named materials that is an array of materials. In the
case of our THREE.BoxGeometry, this array contains 6
materials, one for each side of the box (the two triangular faces for
each side have the same material). You need to
change one of the materials in this array to be
a THREE.MeshLambertMaterial with appropriate values for
the
color, side, and map properties.
Your solution might look like this room-with-view-v2.html
Why do you think the window appears with its hinge on the left side here, rather than on the right side, as it appeared in the first solution?
Next Time: Repeating Textures, the Texture Tutor, and Synthetic Textures
Texture patterns can also be repeated on an object geometry. Next time, we'll explore this tutor for texture mapping, based on a tutor by Nate Robins, which illustrates key ideas that include the creation of repetitive textures:
Some key concepts are:
- the difference between repeat/clamp/mirror
- the meaning of texture coordinates
sandt.tgoes from bottom to top in the above demonstration. (Ignore thetvalues in the image, because it's been flipped.) - the meaning of
flipY
Next time, we'll also explore how to create our own synthetic images to use for texture mapping.