

|
 |
 |
 |
| Home | Advanced Search | Options | Contact |
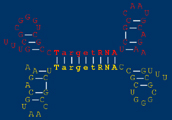
Many small, non-coding RNAs (sRNAs) act as post-transcriptional regulators of messenger RNAs by base-pair binding to these targets.  is a program which, given the sequence of a small RNA gene, searches the entire genome of a species for potential targets of the sRNA gene's action. is a program which, given the sequence of a small RNA gene, searches the entire genome of a species for potential targets of the sRNA gene's action.
|
| Species | The genome in which  searches for targets of the given sRNA gene. searches for targets of the given sRNA gene. |
| sRNA |  provides a list of known sRNA genes (the list, of course, is incomplete). The user has the option of searching for targets of one of these known sRNA genes or else searching for targets of an sRNA gene whose sequence is input by the user. provides a list of known sRNA genes (the list, of course, is incomplete). The user has the option of searching for targets of one of these known sRNA genes or else searching for targets of an sRNA gene whose sequence is input by the user. |
| sRNA Sequence | The user inputs the nucleotide sequence of an sRNA gene.  will search for targets of this sRNA gene's action. will search for targets of this sRNA gene's action. |
| Remove terminator |  will automatically identify and remove the terminator stem-loop of the sRNA sequence. Often, the terminator stem-loop does not participate in the sRNA:mRNA interaction. will automatically identify and remove the terminator stem-loop of the sRNA sequence. Often, the terminator stem-loop does not participate in the sRNA:mRNA interaction. |
| Focus around start codon | Many sRNAs interact with their target genes around the targets' translation start sites and ribosome binding sites. The user can restrict the search for target interaction to the neighborhood around a message's start codon. If the user enters the sentinel neighborhood (0,0) then the program will search the entire coding sequence of a gene for a target interaction. |
| Hybridization seed |  will only report target interactions which contain at least a certain number of consecutive base-pairings as specified by the hybridization seed. To obtain all target interactions, the user should set the hybridization seed to 0. will only report target interactions which contain at least a certain number of consecutive base-pairings as specified by the hybridization seed. To obtain all target interactions, the user should set the hybridization seed to 0. |
| G:U pairs in seed | Allow G:U basepairs when determining the consecutive base-pairings in a hybridization seed. |
| Single target | Rather than search an entire genome for target interactions with the given sRNA,  will only search for an interaction with one particular gene as specified by the gene's name. will only search for an interaction with one particular gene as specified by the gene's name. |
| P-value threshold | Only report target interactions with a P-value below this threshold. |
| Thermodynamic energy scoring |  will identify and score targets based on the minimum free energy of the target interaction with the sRNA gene. The energy of the hybridization is calculated using the thermodynamic parameters employed by MFOLD version 3.0 (Zuker, Nucleic Acids Research, 31 (13), 3406-15, 2003). will identify and score targets based on the minimum free energy of the target interaction with the sRNA gene. The energy of the hybridization is calculated using the thermodynamic parameters employed by MFOLD version 3.0 (Zuker, Nucleic Acids Research, 31 (13), 3406-15, 2003). |
| Orthologous genes | For a given sRNA gene,  will first attempt to identify orthologous sRNA genes in related species (generally, orthologous sRNAs are found only in closely related species). If an orthologous sRNA gene is found in another species' genome, then will first attempt to identify orthologous sRNA genes in related species (generally, orthologous sRNAs are found only in closely related species). If an orthologous sRNA gene is found in another species' genome, then  will determine the hybridization of the ortholgous sRNA to orthologous mRNA targets. will determine the hybridization of the ortholgous sRNA to orthologous mRNA targets. |